Cardiovascular Disease Risk (APOE) DNA Testing:
Find out if you are at increased risk
- Cardiovascular diseases are conditions that affect the blood vessels and can lead to chest pain, heart attacks and strokes
- Your APOE genotype could put you at risk of high cholesterol or hyperlipoproteinemia – both increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease
- Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent cardiovascular disease
- Simple mouth swab DNA test with results in 1 – 2 weeks
What is Cardiovascular Disease Risk (APOE) DNA Testing?

The three most common alleles of APOE are e2, e3 and e4 and each produce a slightly different version of the ApoE protein. This cardiovascular disease (APOE) DNA test is able to determine what APOE alleles an individual has. This genotype provides an indication of cardiovascular disease risk and also the best treatment option to reduce this risk.
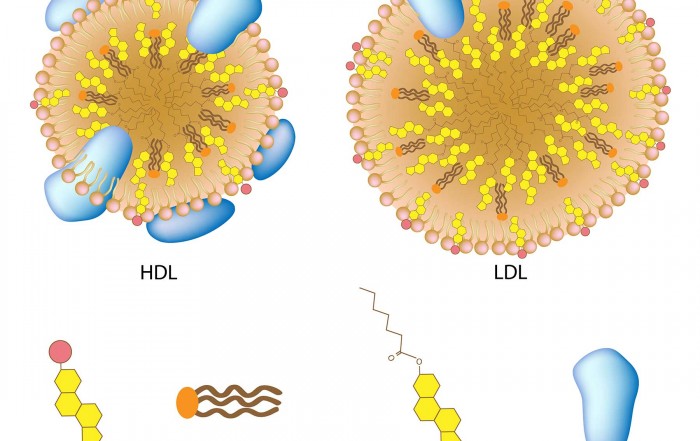
- APOE e2 – The e2 allele is associated with lower LDL-cholesterol levels, but an increased risk for hyperlipoproteinemia type III (in homozygotes). If a person with this allele has high blood cholesterol, they may not respond very effectively to a low-fat diet, but statins are generally an effective treatment option.
- APOE e3 — The common e3 allele is a neutral allele and is not associated with elevated LDL-cholesterol or hyperlipoproteinemia type III. If a person with this allele has high blood cholesterol, they will benefit from a low-fat diet and statins are also generally an effective treatment option.
- APOE e4 — The e4 allele is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease due to elevated LDL-cholesterol levels. If a person with this allele has high blood cholesterol, they will benefit from adapting a low-fat diet, but statins are unlikely to be an effective treatment option.
Step-by-Step
The kit can be ordered online, by fax or mail, or by phone. Once you place the order, the testing kit will be shipped directly to you. The kit contains swabs called “buccal swabs”. DNA is collected quickly and easily by rubbing the swabs inside your mouth against the cheek for 30 seconds. Once the DNA is collected, the swabs are placed into the specimen container provided in the kit and returned to the laboratory for testing using the return package included in the testing kit. Once your samples arrive at the laboratory, testing begins immediately and results are available in 1 to 2 weeks.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
Elevated LDL-Cholesterol Levels:
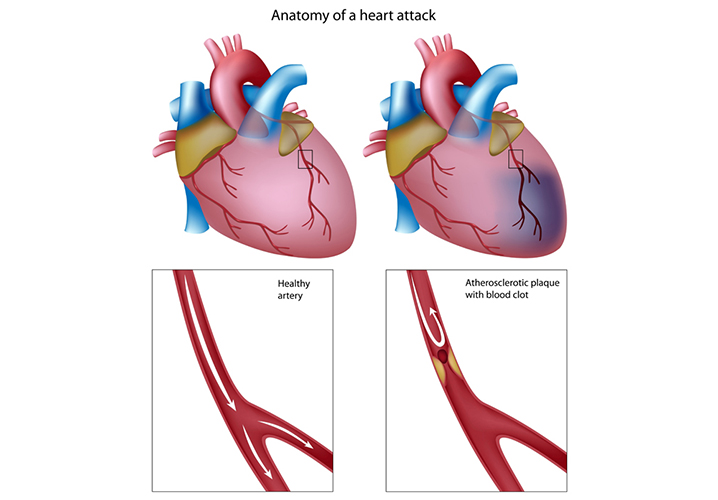
High cholesterol is often a “silent” condition as there may be no early warning of the fatty deposits and plaques until serious complications occur (e.g. heart attack).
Hyperlipoproteinemia Type III:
Hyperlipoproteinemia symptoms vary between individuals and some people may not show any symptoms at all. Often a secondary factor (genetic or environmental) is required before symptoms appear.
- Plaques, atherosclerosis, angina, peripheral vascular disease, heart and stroke risks (as per the symptoms of elevated LDL-cholesterol)
- Xanthomas (lipid deposits forming yellow bumps on, or just beneath, the skin)
- Xanthoma striata palmaris (xanthomas on the palms of the hands)
- Arcus lidus corneae (fatty deposits within the corneas)
- Hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver or spleen)
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas causing back pain, diarrhea, jaundice and sometimes diabetes)
Frequently Asked Questions
Get Started
Cardiovascular Disease Learning Center
What is Apolipoprotein E?
Apolipoproteins are proteins that have binding affinity for lipids to form packages called lipoproteins. They are responsible for transporting lipids through the lymphatic and circulatory systems. The APOE gene encodes the Apolipoprotein E protein, which [...]
What are the signs and symptoms of Type III Hyperlipoproteinemia?
Type III hyperlipoproteinemia is a genetic disorder characterized by high blood cholesterol and triglycerides, leading to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms of Type III hyperlipoproteinemia vary in severity. The symptoms for this disorder [...]
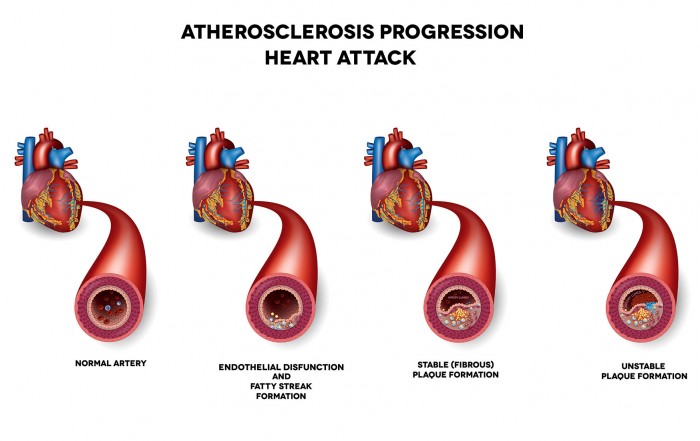
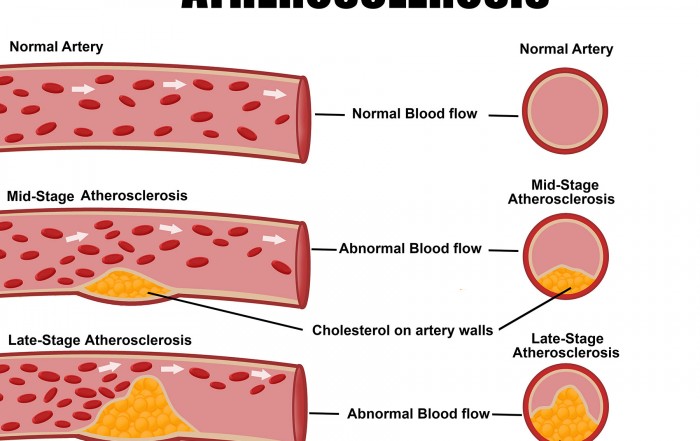
What is Atherosclerosis and its associated risk factors?
Atherosclerosis is a condition where plaque progressively builds up in the arteries over time, causing narrowing and hardening of the arteries. Excess LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream accumulates as plaque deposits which restrict or block [...]